Biomass
Within renewable energies, biomass is the oldest known to humankind
Generation
We developed projects for thermal power plants to produce thermal and electrical energy from biomass resources.
Our projects are designed by integrating all the areas related to the fuel extraction process (biomass) up to energy generation, going through the following stages:
- Crop management and exploitation of energy farms.
- Transportation
- Crushing of biomass according to its nature, moisture, and size.
- Storage.
- Feed into the Boiler.
- Feed into the Boiler furnace.
- Combustion.
- Ventilation.
- Emission control.



Services
TYPES OF BIOMASS
Energy Crops
Certain crops can be produced with the primary or sole purpose of being turned into biomass for fuel. Examples include Acacia Mangium, Eucalyptus, Bamboo, Arundo Donax, and Giant King Grass.
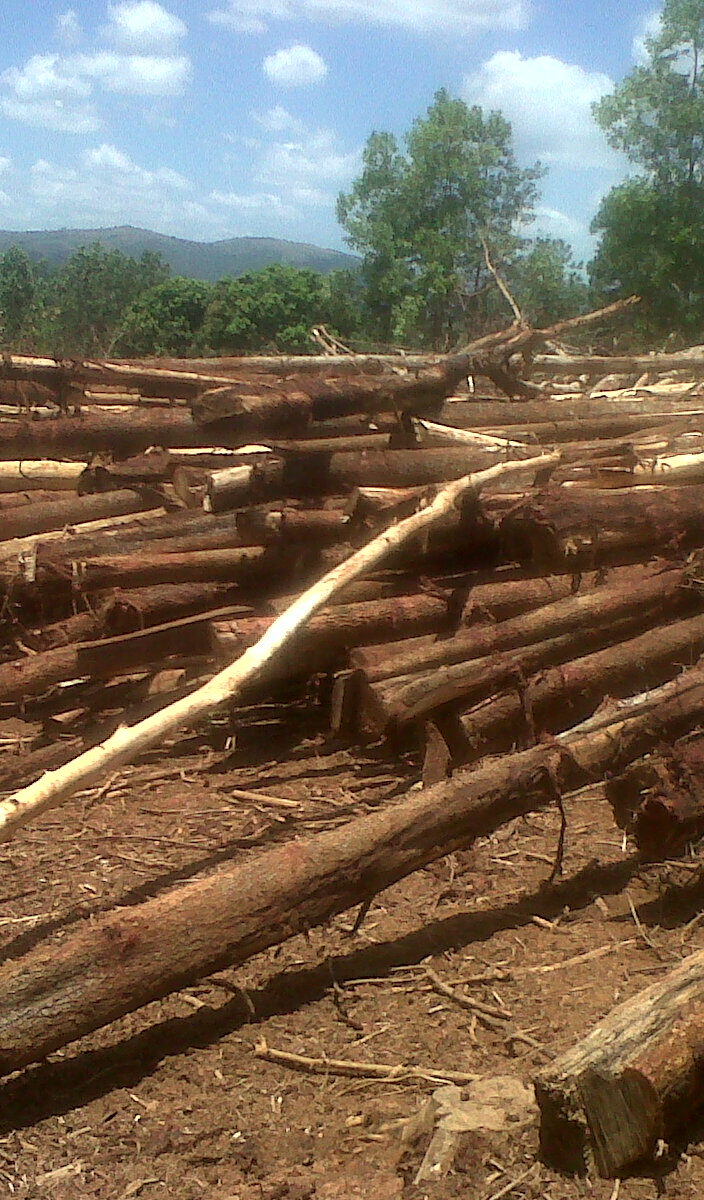
Forest Residue Biomass
They are produced naturally without human intervention. Examples include natural pruning.
Agricultural Residue Biomass
Agricultural residue biomass is the biomass generated from farming activities. Our company has successfully documented that the use of farm residues developed from woody or herbaceous crops can also be turned into biomass.
Agroindustrial Residue Biomass
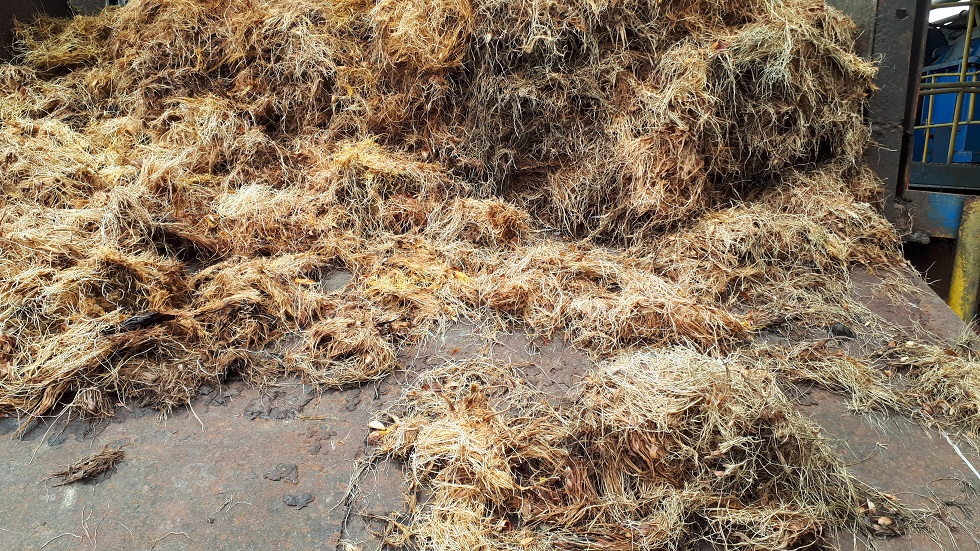
Agroindustrial residue biomass refers to the waste generated in the agroindustrial production process that is successfully turned into a primary biomass fuel source.
Some examples of agroindustrial residues suited for biomass are sugarcane bagasse, rachis, mesocarp, coconut husk and shell, fruit shell, olive pit, corn cob, and rice husk, among other similar residue types.
